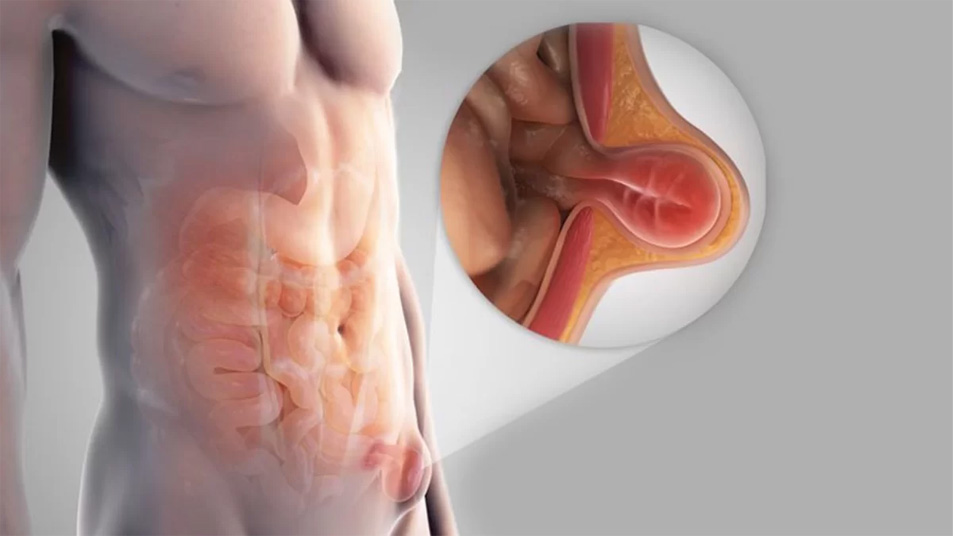
Inguinal Hernia Surgery, Umbilical Hernia Treatment in Konkan
Inguinal and Umbilical Hernia surgeries are procedures performed to repair hernias in specific areas of the body. A hernia occurs when an internal part of the body pushes through a weakness in the muscle or surrounding tissue wall.
Inguinal Hernia Surgery
About Inguinal Hernia
Inguinal Hernia occurs in the groin area, where part of the intestine or fatty tissue protrudes through a weak spot in the abdominal muscles. Men are more prone to Inguinal Hernia than women. Inguinal hernia surgery is a well-established and generally safe procedure that effectively addresses the condition. Advancement in surgical techniques, particularly laparoscopic methods, have improved recovery times and reduced complications. As with any surgery, it is important to discuss the options, risks, and benefits with a healthcare provider to determine the best approach for individual cases.
Causes of Inguinal Hernia :
When there is a weakening or hole in your lower abdominal wall that permits abdominal tissue to protrude through, it might result in an inguinal hernia. Numerous factors may be involved in this, such as:
- A vulnerability or hole that exists from birth.
- Congenital variations in the collagen (connective tissue) strength.
- Weakness or opening following prior abdominal surgery.
- Persistent sneezing or coughing.
- Persistent feces or pee straining.
- Regular hard physical activity or manual labor.
- Years of carrying tiny children and being pregnant.
- Jobs where standing is required for extended periods of time.
- Abdominal pressure brought on by long-term obesity.
- Normal tissue deterioration associated with aging.
About Inguinal Hernia Surgery
The main objective of Inguinal Hernia Surgery is to relocate the hernia's contents back into your abdominal cavity and seal the opening. Surgeons adapt Hernioplasty procedure by using a tiny synthetic mesh or tissue from another area of your body to strengthen the weak place.
Hernia repair is one of the most popular surgical operations carried out globally and is frequently completed as outpatient surgery. Anesthesia might be used locally, regionally, or generally for the procedure.
The patient is given general anesthesia before the surgery. From the waist down, regional anesthesia causes numbness in the body. Local anesthesia numbs only the part of your body being operated on, in this case, your groin.
Types of Inguinal Hernia Surgery :
The type of surgery will depend on patients condition, previous surgical history, and the experience and judgment of the surgeon.
Open Inguinal Hernia Repair (Herniorrhaphy or Hernioplasty) :
The surgeon makes an incision in the groin and pushes the protruding tissue back into the abdomen. The muscle wall is then reinforced with stitches, and often a synthetic mesh is placed to provide additional support and prevent recurrence.
The patients have to stay in the hospital of a few days, with complete recovery in about 4-6 weeks.
Laparoscopic Inguinal Hernia Repair :
This minimally invasive surgery involves several small incisions through which the surgeon inserts a laparoscope (a thin tube with a camera) and surgical instruments. The hernia is repaired from the inside, usually with the placement of mesh.
Benefits of this method include smaller incisions, less postoperative pain, Lower risk of infection and a quicker recovery time. Recovery involves a shorter hospital stay and quicker recovery time (1-2 weeks) compared to open surgery.
Postoperative Care :
Pain Management : Pain and discomfort are common after hernia surgery, and pain relief medication is usually prescribed.
Activity Restrictions : Patients are advised to avoid heavy lifting and strenuous activities for several weeks to allow proper healing.
Follow-Up : Regular follow-up visits are crucial to monitor recovery and detect any complications early.
Prognosis :
The prognosis after inguinal hernia surgery is generally very good, with most patients experiencing relief from symptoms and a low rate of recurrence, especially when mesh is used in the repair.
Umbilical Hernia Surgery
About Umbilical Hernia
The umbilical ring, a tiny gap in a baby's abdominal muscles through which the umbilical cord which links a fetus to its mother while in the womb passes is where an umbilical hernia forms at the umbilicus (belly button). Ninety percent of umbilical hernias spontaneously heal by the time the kid becomes five years old. These hernias mostly affect infants.
Cause of Umbilical Hernia :
The umbilical cord is no longer required after delivery, and as the infant becomes older, the abdominal muscle opening closes. These muscles can occasionally fail to meet perfectly, creating a little opening. A hernia can result from an intestinal loop moving into or even into the space between abdominal muscles. Although they can develop in adults as well, umbilical hernias mostly affect babies.
Adult cases of umbilical hernias are most frequently caused by Chronic illnesses that increase the pressure in the abdomen include :
- Having an overabundance of abdominal fluid (ascites)
- Persistent cough
- Urinary difficulties brought on by an enlarged prostate
- Prolonged constipation
- Frequent episodes of vomiting
- Being overweight
- Exerting oneself, as in giving birth or moving heavy objects
About Umbilical Hernia Surgery :
Umbilical Hernia surgery is a procedure to correct an umbilical hernia, a condition where part of the intestine or fatty tissue protrudes through an opening in the abdominal muscles near the navel (umbilicus). An Umbilical Hernia occurs near the navel (belly button), where part of the intestine or fatty tissue pushes through the abdominal muscle near the umbilicus.
An incision is made near the umbilicus (for open surgery) or several small incisions are made for laparoscopic access. The herniated tissue is pushed back into the abdominal cavity. Sutures are used to seal abdominal wall defect. A synthetic mesh may be placed over the defect to reinforce the area and reduce the risk of recurrence. Staples or sutures are used to seal the wounds.
This type of hernia is common in infants but can also occur in adults, particularly in women after childbirth or in individuals with increased abdominal pressure due to obesity or heavy lifting.
Diagnosis of Umbilical Hernia :
A Health Care professional will often identify a hernia via a physical examination. The healthcare professional will feel and inspect for any edema or bulging at the abdominal button. When a baby screams, the swelling can be more apparent, and when it relaxes or lies on its back, it might lessen or go entirely. The doctor will assess if the hernia can be forced back into the abdominal cavity, or whether it is reducible, during the examination.
In order to ascertain whether the umbilical hernia has been incarcerated that is, imprisoned within the abdominal opening a dangerous medical condition in which the projecting intestine becomes stuck and loses its blood supply the healthcare professional will also check for and complete a medical history. Necrosis of the gut can occur rapidly if untreated.
The provider may order blood tests to look for signs of infection resulting from the strangulated intestine. They may also order a barium X-ray, ultrasound, MRI or CT to examine the intestine more closely, especially if the hernia is no longer reducible.
Types of Umbilical Hernia Surgery :
Open Umbilical Hernia Repair :
The surgeon makes an incision at the base of the belly button and pushes the protruding tissue back into the abdomen. The muscle wall is then closed with stitches, and a mesh may be placed to reinforce the area.
Laparoscopic Umbilical Hernia Repair :
Similar to laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair, small incisions are made, and the procedure is performed using a laparoscope and surgical instruments. The hernia is repaired with or without the use of mesh.
Postoperative Care :
The patient is monitored in the recovery room until the effects of anesthesia wear off. Pain management is provided as needed.
Hospital Stay : This can be an outpatient procedure, but some patients may need to stay overnight, especially if there are complications or significant comorbidities.
At Home : Patients are advised to avoid strenuous activities and heavy lifting for several weeks. They are encouraged to walk and engage in light activities to prevent blood clots and promote healing.
Follow-Up : A follow-up appointment is scheduled to monitor the healing process and remove stitches if necessary.
Prognosis :
The prognosis after umbilical hernia surgery is generally good. Most patients recover fully and can return to their normal activities within a few weeks. The use of mesh has significantly reduced the rate of recurrence.
A patient before undergoing Umbilical Hernia Surgery must consult with a qualified healthcare provider to discuss the best treatment approach based on individual health conditions and the specifics of the hernia.
